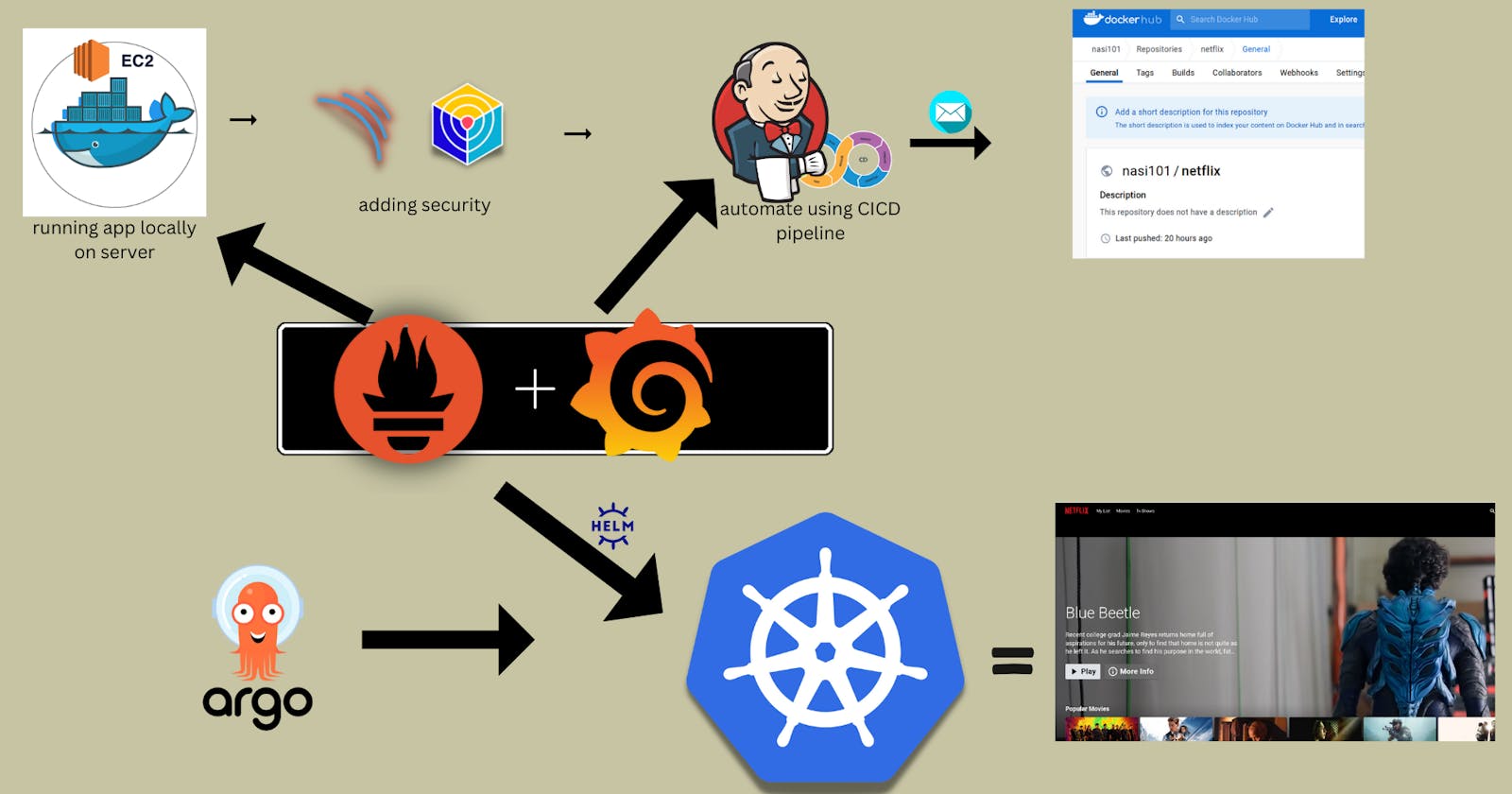
Deploy Netflix clone app on AWS using automated Jenkins CI/CD and deploy it on Kubernetes using Argo CD (GitOPs tool) following DevSecOps practices
SonarQube, Trivy (file & image scan), OWASP, NPM dep, Prometheus, Grafana, SNS (Simple Notification Service), EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service), Argo,
The structure for the steps and objectives of the DevSecOps project, outlining the progression and goals of each phase.
Set up an AWS EC2 T2 Large instance for Jenkins, SonarQube, and Trivy.
set up an AWS EC2 T2 Medium instance for the monitoring server.
Install and configure Jenkins CICD pipeline with security.
Create Dockerfiles for applications. Set up the Docker build process in Jenkins then Push Docker images to Docker Hub.
Install monitoring tools (e.g., Prometheus, Grafana) on the EC2 T2 Medium instance—Configure monitoring for the monitoring server and Jenkins—Set up alerts and notifications—Enable the monitoring for the server and Jenkins.
Provision of an Amazon EKS cluster for application deployment.
Set up email notification alerts using AWS SNS or another service.
Divided into 6 Phases
Phase 1: Initial Setup and Deployment
Launching EC2 Instances # requirements
T2 large
30FROM node:16.17.0-alpine as builder WORKDIR /app COPY ./package.json . COPY ./yarn.lock . RUN yarn install COPY . . ARG TMDB_V3_API_KEY ENV VITE_APP_TMDB_V3_API_KEY=${d35af87eeb9a8cf7d471d291ebc7331e} ENV VITE_APP_API_ENDPOINT_URL="https://api.themoviedb.org/3" RUN yarn build FROM nginx:stable-alpine WORKDIR /usr/share/nginx/html RUN rm -rf ./* COPY --from=builder /app/dist . EXPOSE 80 ENTRYPOINT ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
-
Install SonarQube and trivy to scan the code quilaty and vulnerabilities
docker run -d --name sonar -p 9000:9000 sonarqube:lts-communityTo access:
publicIP:9000 (by default username & password is admin)

To install Trivy:
sudo apt-get install wget apt-transport-https gnupg lsb-release wget -qO - https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb/public.key | sudo apt-key add - echo deb https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb $(lsb_release -sc) main | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/trivy.list sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install trivyto scan image using trivy
trivy fs . # for all trivy image <image_ID> #
Install Jenkins for Automation:
- Install Jenkins on the EC2 instance to automate deployment: Install Java
sudo apt update
sudo apt install fontconfig openjdk-17-jre
java -version
openjdk version "17.0.8" 2023-07-18
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 17.0.8+7-Debian-1deb12u1)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 17.0.8+7-Debian-1deb12u1, mixed mode, sharing)
#jenkins
sudo wget -O /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
sudo systemctl start jenkins
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
Access Jenkins in a web browser using the public IP of your EC2 instance.
publicIp:8080
Install Necessary Plugins in Jenkins:
/Goto Manage Jenkins →Plugins → Available Plugins →
1 Eclipse Temurin Installer (Install without restart)
2 SonarQube Scanner (Install without restart)
3 NodeJs Plugin (Install Without restart)
4 Email Extension Plugin
sudo apt update sudo apt install fontconfig openjdk-17-jre java -version openjdk version "17.0.8" 2023-07-18 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 17.0.8+7-Debian-1deb12u1) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 17.0.8+7-Debian-1deb12u1, mixed mode, sharing) #jenkins sudo wget -O /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkins sudo systemctl start jenkins sudo systemctl enable jenkins

Access Jenkins in a web browser using the public IP of your EC2 instance.
publicIp:8080

Configure Java and Nodejs in Global Tool Configuration
Goto Manage Jenkins → Tools → Install JDK(17) and NodeJs(16)→ Click on Apply and Save
SonarQube
Create the token
Goto Jenkins Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Credentials → Add Secret Text. It should look like this
After adding sonar token
Click on Apply and Save
The Configure System option is used in Jenkins to configure different server
Global Tool Configuration is used to configure different tools that we install using Plugins
We will install a sonar scanner in the tools.
Create a Jenkins webhook
- Configure CI/CD Pipeline in Jenkins:
- Create a CI/CD pipeline in Jenkins to automate your application deployment.
pipeline { agent any tools { jdk 'jdk17' nodejs 'node16' } environment { SCANNER_HOME = tool 'sonar-scanner' } stages { stage('clean workspace') { steps { cleanWs() } } stage('Checkout from Git') { steps { git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/N4si/DevSecOps-Project.git' } } stage("Sonarqube Analysis") { steps { withSonarQubeEnv('sonar-server') { sh '''$SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=Netflix \ -Dsonar.projectKey=Netflix''' } } } stage("quality gate") { steps { script { waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: false, credentialsId: 'Sonar-token' } } } stage('Install Dependencies') { steps { sh "npm install" } } } }
Certainly, here are the instructions without step numbers:
Install Dependency-Check and Docker Tools in Jenkins
Install Dependency-Check and Docker Tools in Jenkins
Install Dependency-Check Plugin:
Go to "Dashboard" in your Jenkins web interface.
Navigate to "Manage Jenkins" → "Manage Plugins."
Click on the "Available" tab and search for "OWASP Dependency-Check."
Check the checkbox for "OWASP Dependency-Check" and click on the "Install without restart" button.
Configure Dependency-Check Tool:
After installing the Dependency-Check plugin, you need to configure the tool.
Go to "Dashboard" → "Manage Jenkins" → "Global Tool Configuration."
Find the section for "OWASP Dependency-Check."
Add the tool's name, e.g., "DP-Check."
Save your settings.
Install Docker Tools and Docker Plugins:
Go to "Dashboard" in your Jenkins web interface.
Navigate to "Manage Jenkins" → "Manage Plugins."
Click on the "Available" tab and search for "Docker."
Check the following Docker-related plugins:
Docker
Docker Commons
Docker Pipeline
Docker API
docker-build-step
Click on the "Install without restart" button to install these plugins.

Add DockerHub Credentials:
To securely handle DockerHub credentials in your Jenkins pipeline, follow these steps:
Go to "Dashboard" → "Manage Jenkins" → "Manage Credentials."
Click on "System" and then "Global credentials (unrestricted)."
Click on "Add Credentials" on the left side.
Choose "Secret text" as the kind of credentials.
Enter your DockerHub credentials (Username and Password) and give the credentials an ID (e.g., "docker").
Click "OK" to save your DockerHub credentials.
Now, you have installed the Dependency-Check plugin, configured the tool, and added Docker-related plugins along with your DockerHub credentials in Jenkins. You can now proceed with configuring your Jenkins pipeline to include these tools and credentials in your CI/CD process.
pipeline{
agent any
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
nodejs 'node16'
}
environment {
SCANNER_HOME=tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('clean workspace'){
steps{
cleanWs()
}
}
stage('Checkout from Git'){
steps{
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/N4si/DevSecOps-Project.git'
}
}
stage("Sonarqube Analysis "){
steps{
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar-server') {
sh ''' $SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=Netflix \
-Dsonar.projectKey=Netflix '''
}
}
}
stage("quality gate"){
steps {
script {
waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: false, credentialsId: 'Sonar-token'
}
}
}
stage('Install Dependencies') {
steps {
sh "npm install"
}
}
stage('OWASP FS SCAN') {
steps {
dependencyCheck additionalArguments: '--scan ./ --disableYarnAudit --disableNodeAudit', odcInstallation: 'DP-Check'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: '**/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}
stage('TRIVY FS SCAN') {
steps {
sh "trivy fs . > trivyfs.txt"
}
}
stage("Docker Build & Push"){
steps{
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker', toolName: 'docker'){
sh "docker build --build-arg TMDB_V3_API_KEY=<yourapikey> -t netflix ."
sh "docker tag netflix nasi101/netflix:latest "
sh "docker push nasi101/netflix:latest "
}
}
}
}
stage("TRIVY"){
steps{
sh "trivy image nasi101/netflix:latest > trivyimage.txt"
}
}
stage('Deploy to container'){
steps{
sh 'docker run -d --name netflix -p 8081:80 nasi101/netflix:latest'
}
}
}
}
If you get docker login failed errorr
sudo su
sudo usermod -aG docker jenkins
sudo systemctl restart jenkins
Phase 4: Monitoring
Install Prometheus and Grafana:
Set up Prometheus and Grafana to monitor your application.
Pometheus
Installing Prometheus:
First, create a dedicated Linux user for Prometheus and download Prometheus:
sudo useradd --system --no-create-home --shell /bin/false prometheus
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.47.1/prometheus-2.47.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Extract Prometheus files, move them, and create directories:
tar -xvf prometheus-2.47.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
cd prometheus-2.47.1.linux-amd64/
sudo mkdir -p /data /etc/prometheus
sudo mv prometheus promtool /usr/local/bin/
sudo mv consoles/ console_libraries/ /etc/prometheus/
sudo mv prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Set ownership for directories:
sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/ /data/
Create a systemd unit configuration file for Prometheus:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service
Add the following content to the prometheus.service file:
[Unit]
Description=Prometheus
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
StartLimitIntervalSec=500
StartLimitBurst=5
[Service]
User=prometheus
Group=prometheus
Type=simple
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5s
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \
--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
--storage.tsdb.path=/data \
--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \
--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries \
--web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9090 \
--web.enable-lifecycle
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Here's a brief explanation of the key parts in this prometheus.service file:
UserandGroupspecify the Linux user and group under which Prometheus will run.ExecStartis where you specify the Prometheus binary path, the location of the configuration file (prometheus.yml), the storage directory, and other settings.web.listen-addressconfigures Prometheus to listen on all network interfaces on port 9090.web.enable-lifecycleallows for management of Prometheus through API calls.
Enable and start Prometheus:
sudo systemctl enable prometheus
sudo systemctl start prometheus
Verify Prometheus's status:
sudo systemctl status prometheus
You can access Prometheus in a web browser using your server's IP and port 9090:
http://<your-server-ip>:9090
Installing Node Exporter:
Create a system user for Node Exporter and download Node Exporter:
sudo useradd --system --no-create-home --shell /bin/false node_exporter
wget https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.6.1/node_exporter-1.6.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Extract Node Exporter files, move the binary, and clean up:
tar -xvf node_exporter-1.6.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo mv node_exporter-1.6.1.linux-amd64/node_exporter /usr/local/bin/
rm -rf node_exporter*
Create a systemd unit configuration file for Node Exporter:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.service
Add the following content to the node_exporter.service file:
[Unit]
Description=Node Exporter
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
StartLimitIntervalSec=500
StartLimitBurst=5
[Service]
User=node_exporter
Group=node_exporter
Type=simple
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5s
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/node_exporter --collector.logind
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Replace --collector.logind with any additional flags as needed.
Enable and start Node Exporter:
sudo systemctl enable node_exporter
sudo systemctl start node_exporter
Verify the Node Exporter's status:
sudo systemctl status node_exporter
You can access Node Exporter metrics in Prometheus.
Configure Prometheus Plugin Integration:
Integrate Jenkins with Prometheus to monitor the CI/CD pipeline.
Prometheus Configuration:
To configure Prometheus to scrape metrics from Node Exporter and Jenkins, you need to modify the
prometheus.ymlfile. Here is an exampleprometheus.ymlconfiguration for your setup:global: scrape_interval: 15s scrape_configs: - job_name: 'node_exporter' static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9100'] - job_name: 'jenkins' metrics_path: '/prometheus' static_configs: - targets: ['<your-jenkins-ip>:<your-jenkins-port>']Make sure to replace
<your-jenkins-ip>and<your-jenkins-port>with the appropriate values for your Jenkins setup.Check the validity of the configuration file:
promtool check config /etc/prometheus/prometheus.ymlReload the Prometheus configuration without restarting:
curl -X POST http://localhost:9090/-/reloadYou can access Prometheus targets at:
http://<your-prometheus-ip>:9090/targets
Grafana
Install Grafana on Ubuntu 22.04 and Set it up to Work with Prometheus
Step 1: Install Dependencies:
First, ensure that all necessary dependencies are installed:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https software-properties-common
Step 2: Add the GPG Key:
Add the GPG key for Grafana:
wget -q -O - https://packages.grafana.com/gpg.key | sudo apt-key add -
Step 3: Add Grafana Repository:
Add the repository for Grafana stable releases:
echo "deb https://packages.grafana.com/oss/deb stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/grafana.list
Step 4: Update and Install Grafana:
Update the package list and install Grafana:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install grafana
Step 5: Enable and Start Grafana Service:
To automatically start Grafana after a reboot, enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable grafana-server
Then, start Grafana:
sudo systemctl start grafana-server
Step 6: Check Grafana Status:
Verify the status of the Grafana service to ensure it's running correctly:
sudo systemctl status grafana-server
Step 7: Access Grafana Web Interface:
Open a web browser and navigate to Grafana using your server's IP address. The default port for Grafana is 3000. For example:
http://<your-server-ip>:3000
You'll be prompted to log in to Grafana. The default username is "admin," and the default password is also "admin."
Step 8: Change the Default Password:
When you log in for the first time, Grafana will prompt you to change the default password for security reasons. Follow the prompts to set a new password.
Step 9: Add Prometheus Data Source:
To visualize metrics, you need to add a data source. Follow these steps:
Click on the gear icon (⚙️) in the left sidebar to open the "Configuration" menu.
Select "Data Sources."
Click on the "Add data source" button.
Choose "Prometheus" as the data source type.
In the "HTTP" section:
Set the "URL" to
http://localhost:9090(assuming Prometheus is running on the same server).Click the "Save & Test" button to ensure the data source is working.
Step 10: Import a Dashboard:
To make it easier to view metrics, you can import a pre-configured dashboard. Follow these steps:
Click on the "+" (plus) icon in the left sidebar to open the "Create" menu.
Select "Dashboard."
Click on the "Import" dashboard option.
Enter the dashboard code you want to import (e.g., code 1860).
Click the "Load" button.
Select the data source you added (Prometheus) from the dropdown.
Click on the "Import" button.
You should now have a Grafana dashboard set up to visualize metrics from Prometheus.
Grafana is a powerful tool for creating visualizations and dashboards, and you can further customize it to suit your specific monitoring needs.
That's it! You've successfully installed and set up Grafana to work with Prometheus for monitoring and visualization.
Configure Prometheus Plugin Integration:
- Integrate Jenkins with Prometheus to monitor the CI/CD pipeline.
Phase 5: Notification
Implement Notification Services:
- Set up email notifications in Jenkins or other notification mechanisms.
- Artifact Management and Deployment
Phase 4: Monitoring
Setting up Monitoring Server
Monitoring Jenkins and EC2 Instances
Phase 5: Notification Setup
- Email Notifications
Phase 6: Kubernetes Deployment
Create Kubernetes Cluster with Nodegroups
In this phase, you'll set up a Kubernetes cluster with node groups. This will provide a scalable environment to deploy and manage your applications.
Monitor Kubernetes with Prometheus
Prometheus is a powerful monitoring and alerting toolkit, and you'll use it to monitor your Kubernetes cluster. Additionally, you'll install the node exporter using Helm to collect metrics from your cluster nodes.
Install Node Exporter using Helm
To begin monitoring your Kubernetes cluster, you'll install the Prometheus Node Exporter. This component allows you to collect system-level metrics from your cluster nodes. Here are the steps to install the Node Exporter using Helm:
Add the Prometheus Community Helm repository:
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-chartsCreate a Kubernetes namespace for the Node Exporter:
kubectl create namespace prometheus-node-exporterInstall the Node Exporter using Helm:
helm install prometheus-node-exporter prometheus-community/prometheus-node-exporter --namespace prometheus-node-exporter
Add a Job to Scrape Metrics on nodeip:9001/metrics in prometheus.yml:
Update your Prometheus configuration (prometheus.yml) to add a new job for scraping metrics from nodeip:9001/metrics. You can do this by adding the following configuration to your prometheus.yml file:
- job_name: 'Netflix'
metrics_path: '/metrics'
static_configs:
- targets: ['node1Ip:9100']
Replace 'your-job-name' with a descriptive name for your job. The static_configs section specifies the targets to scrape metrics from, and in this case, it's set to nodeip:9001.
Don't forget to reload or restart Prometheus to apply these changes to your configuration.
To deploy an application with ArgoCD, you can follow these steps, which I'll outline in Markdown format:
Deploy Application with ArgoCD
Install ArgoCD:
You can install ArgoCD on your Kubernetes cluster by following the instructions provided in the EKS Workshop documentation.
Set Your GitHub Repository as a Source:
After installing ArgoCD, you need to set up your GitHub repository as a source for your application deployment. This typically involves configuring the connection to your repository and defining the source for your ArgoCD application. The specific steps will depend on your setup and requirements.
Create an ArgoCD Application:
name: Set the name for your application.destination: Define the destination where your application should be deployed.project: Specify the project the application belongs to.source: Set the source of your application, including the GitHub repository URL, revision, and the path to the application within the repository.syncPolicy: Configure the sync policy, including automatic syncing, pruning, and self-healing.
Access your Application
- To Access the app make sure port 30007 is open in your security group and then open a new tab paste your NodeIP:30007, your app should be running.
Phase 7: Cleanup
Cleanup AWS EC2 Instances:
- Terminate AWS EC2 instances that are no longer needed.